Getting Started with Neomodel
Neomodel is an Object Graph Mapper (OGM) for the Neo4j graph database built on py2neo and provides a Django ORM style definition.
We are going to look at using neomodel in a ‘DevOpsy’ manner using Docker.
Below is our resulting graph:
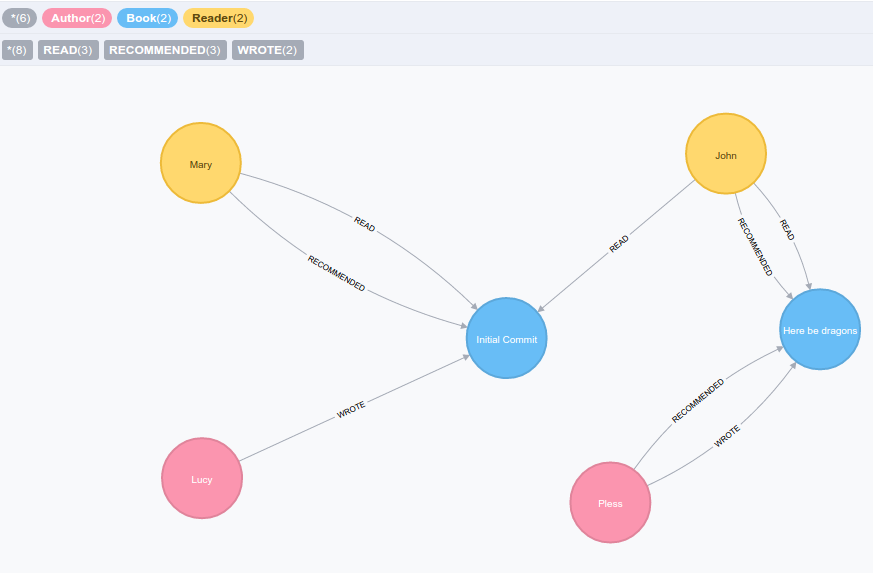
Let’s start by using the Neo4j docker image to get up and running with the neo4j graph database:
I’m assuming that you have docker installed
$ docker run -d \
-p 7474:7474 \
-v $HOME/Desktop/neo4j/data:/data \
--name neomodel_neo4j \
neo4j:2.3.3
This will mount $HOME/Desktop/neo4j/data in our Docker host to /data inside the container.
Point your browser at http://localhost:7474, login with neo4j/neo4j and set a new password.
Installing neomodel
Let’s install neomodel using pip
$ pip install neomodel
Setting the neo4j location
Neomodel requires that we set the location of neo4j via an environment variable, this defaults to http://localhost:7474/db/data/
$ export NEO4J_REST_URL=http://neo4j:password@localhost:7474/db/data/
Defining models and properties
We then define a Python module by the name of model.py and within that define three StructuredNode classes and one StructuredRel class with their properties and relationships. An Author WROTE a Book, and the Reader READ the Book. The Book may also be RECOMMENDED by the Reader reading it, an Author may also recommend a Book that they have written.
StructuredRel is used to define the properties stored on relations.
# model.py
from neomodel import (StructuredNode, StructuredRel,
StringProperty, DateProperty,
RelationshipTo, OneOrMore)
class Recommended(StructuredRel):
date = DateProperty(default=None)
class Author(StructuredNode):
name = StringProperty(Unique_Index=True, required=True)
born = DateProperty()
died = DateProperty(default=None)
wrote = RelationshipTo('Book', 'WROTE', OneOrMore)
recommended = RelationshipTo(
'Book', 'RECOMMENDED', OneOrMore, model=Recommended
)
class Book(StructuredNode):
title = StringProperty(Unique_Index=True, required=True)
published = DateProperty()
class Reader(StructuredNode):
name = StringProperty(Unique_Index=True, required=True)
born = DateProperty()
read = RelationshipTo('Book', 'READ', OneOrMore)
recommended = RelationshipTo(
'Book', 'RECOMMENDED', OneOrMore, model=Recommended
)
Persisting and querying models and properties
With our model in place, let’s define another Python module: ctrlmodel.py.
This will be used to populate and ‘control’ our Neo4j database.
We will start by defining a function that creates the nodes and saves them in our database.
# ctrlmodel.py
from model import *
from neomodel import UniqueProperty, DoesNotExist, db
from datetime import date
class ctrlModel():
def createNodes(self):
try:
# Create Authors
Author(name='Pless', born=date(1900, 01, 01),
died=date(1990, 12, 12)).save()
Author(name='Lucy', born=date(1950, 12, 12)).save()
# Create Books
Book(title='Here be dragons', published=date(1950, 12, 12)).save()
Book(title='Initial Commit', published=date(1990, 12, 12)).save()
# Create Readers
Reader(name='John', born=date(1980, 05, 06)).save()
Reader(name='Mary', born=date(1985, 03, 07)).save()
except UniqueProperty, e:
raise e
We then define another function to search the created nodes by name for the Author and Reader, and title for the Book.
# ctrlmodel.py
def searchNodes(name):
try:
print 'Searching Author Node with Name=', name # Search all nodes with Label Author
node = Author.nodes.get(name=name)
return node
except DoesNotExist, e:
pass
try: # Searching all nodes with Label Book
print 'Searching Book Node with Title=', name
node = Book.nodes.get(title=name)
return node
except DoesNotExist, e:
pass
try:
print 'Searching Reader Node with Name=', name # Search all nodes with Label Reader
node = Reader.nodes.get(name=name)
return node
except DoesNotExist, e:
pass
return None
Let’s add functions that borrow functionality from the above to create relationships between our nodes.
# ctrlmodel.py
class ctrlModel():
def createWroteRel(self):
try:
print 'Creating WROTE relationship between given nodes'
searchNodes('Pless').wrote.connect(
searchNodes('Here be dragons'))
searchNodes('Lucy').wrote.connect(
searchNodes('Initial Commit'))
print 'Creating WROTE relationship between given nodes'
except Exception, e:
raise e
def createReadRel(self):
try:
print 'Creating READ relationship between given nodes'
searchNodes('John').read.connect(
searchNodes('Here be dragons'))
searchNodes('John').read.connect(
searchNodes('Initial Commit'))
searchNodes('Mary').read.connect(
searchNodes('Initial Commit'))
print 'Done creating READ relationship between nodes'
except Exception, e:
raise e
def createRecommendedRel(self):
try:
print 'Creating RECOMMENDED relationship between given nodes'
searchNodes('John').recommended.connect(
searchNodes('Here be dragons'),
{'date': date(1995, 1, 12)})
searchNodes('Pless').recommended.connect(
searchNodes('Here be dragons'),
{'date': date(1997, 11, 1)})
searchNodes('Mary').recommended.connect(
searchNodes('Initial Commit'),
{'date': date(2005, 6, 3)})
print 'Done creating RECOMMENDED relationship between nodes'
except Exception, e:
raise e
I thought I should add another function to delete any existing data before executing our createNodes function. This will help avoid the MultipleNodesReturned exception when searching our database.
# ctrlmodel.py
def deleteData():
print 'Delete all nodes and relationships...'
query = 'MATCH (n) DETACH DELETE n'
db.cypher_query(query)
We then create another Python module and give the name main.py.
from model import *
from ctrlmodel import *
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Start by deleting existing data
deleteData()
create = ctrlModel()
create.ctrlNodes()
create.createWroteRel()
create.createReadRel()
create.createRecommendedRel()
print 'Done!'
Executing our main.py.
$ python main.py
Would give us the graph depicted above.
Thanks to Building Web Applications with Python and Neo4j .

Leave a comment